Abstract
Introduction. Software containers are becoming the new state of the art in the industry as they are extensively used to deploy systems. Indeed, the use of containers enables better modularity, reusability, and portability compared to other technologies. As the complexity of software systems is dramatically increasing, it is critical to enable optimal usage of the needed resources to execute them such as memory and CPU. Thus, different scheduling strategies are proposed to select the most suitable nodes to execute a set of containers. For instance, the default strategy in the Docker Swarm kit scheduling framework is based on an equal distribution of the containers between nodes independent of their sizes and consumed resources. However, balancing the containers’ workload is a complex problem due to the conflicting objectives of minimizing the number of selected nodes, minimizing the number of containers per node, the number of changes compared to the original schedule, and the coupling between containers allocated to different nodes.
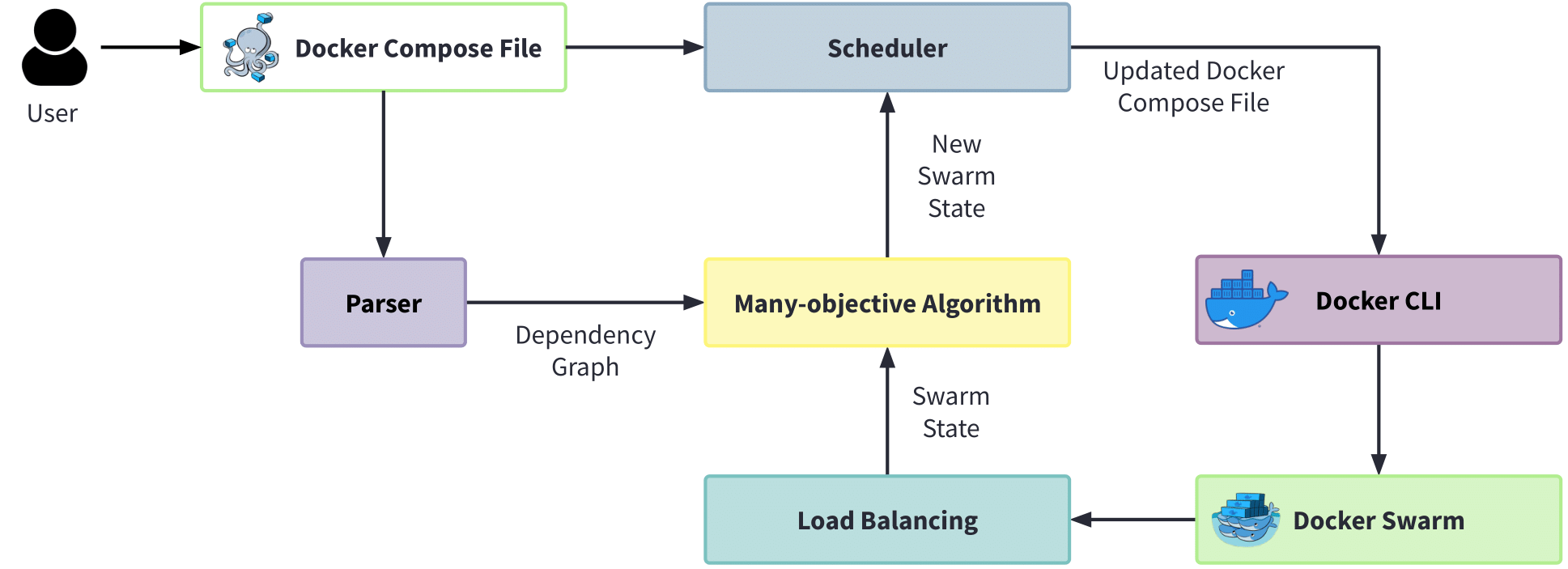
Methods. To deal with those conflicting scheduling objectives, we propose a scheduler based on a many-objective optimization approach for scheduling the execution of containers between multiple nodes. The proposed approach aims at finding the best allocation for containers in nodes that leads to efficient utilization of resources. To evaluate our approach, we compared the performance of multiple many and multi-objective techniques based on NSGA-II, NSGA-III, and IBEA algorithms using 48 Docker-related systems and the results show that NSGA-III outperforms the other algorithms in quality attributes as well as in CPU, Memory and Network usage
Research Questions
RQ1: To what extent can the proposed NSGA-III approach provide efficient scheduling solutions based on different multi-objective (NSGA-II) and many-objective algorithms (IBEA)?
This question aims to investigate the efficiency of our many-objective NSGA-III approach for container scheduling to find trade-offs between the different conflicting objectives compared to other multi/many-objective algorithms.
RQ2: To what extent can the proposed NSGA-III approach minimize the resources consumption in the cluster and balance the software workload (i.e., CPU and memory usage, the network I/O of each node) compared to the deterministic Docker Swarm’s default scheduler?
Since it is not sufficient to validate the outperformance of our approach compared to other search-based algo- rithms, this question evaluates the ability of our approach compared to the deterministic by default scheduler of the Docker Swarm in terms of the resources consumption (i.e., CPU and memory usage).
Overview approach of the study
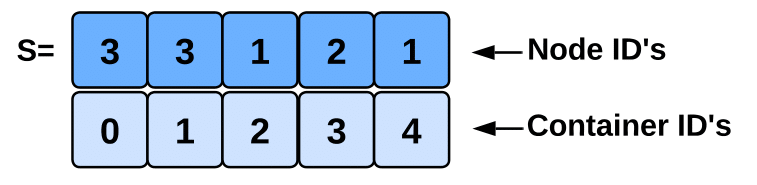
Solution Representation
NSAIII

